Understanding Hip and Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
What Are Hip and Elbow Dysplasia?
Hip Dysplasia is a developmental condition where the hip joint doesn’t fit together properly, causing looseness and abnormal movement.
Elbow Dysplasia refers to abnormal development of the elbow joint, typically involving one or more structural defects, usually caused by one or more of the following:-
-
Fragmented Coronoid Process (FCP):
-
One of the bones in the elbow, the ulna, has a small bony protrusion called the coronoid process.
-
In FCP, this process fractures or breaks away due to uneven growth or pressure.
-
This fragment irritates the joint, causing pain, inflammation, and arthritis.
-
Common in: Large breeds like Labradors and Great Danes.
-
Ununited Anconeal Process (UAP):
-
Another part of the ulna, the anconeal process, is supposed to fuse to the bone by 5 months of age.
-
In UAP, it doesn’t fuse properly, leaving a loose piece in the joint.
-
This loose fragment causes joint instability and pain, often needing surgical correction.
-
More common in: German Shepherds and Basset Hounds.
-
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD):
-
A cartilage development issue where a flap of cartilage separates from the bone, often in the elbow or shoulder.
-
This causes joint pain and may lead to arthritis if the flap detaches completely.
-
Associated with rapid growth, poor diet, and genetic factors.
-
Joint Incongruity:
-
The three bones of the elbow (humerus, radius, ulna) must align perfectly.
-
If they don’t, pressure is unevenly distributed, causing damage and predisposing the joint to conditions like FCP or OCD.
-
Leads to chronic instability and pain.

What can cause elbow or hip dysplasia?
-
Genetics
-
Faulty genes lead to improper bone and joint development.
-
Poor breeding practices perpetuate these genes by ignoring health screening.
-
Line breeding or inbreeding can increase the expression of defective genes.
-
Rapid Growth
-
Large breed puppies often grow too quickly, stressing their joints.
-
Growth plate closure timing can mismatch, causing bone misalignment (joint incongruity).
-
Overfeeding or Poor Diet
-
Diets too rich in calories or calcium/phosphorus imbalance can disrupt bone growth.
-
Puppies given too much protein or energy-rich food may grow faster than their skeleton can handle.
-
Obesity
-
Excess body weight puts tremendous pressure on developing or already malformed joints.
-
This accelerates degeneration and worsens pain and inflammation.
-
High-Impact Exercise in Puppies
-
Jumping, running on hard surfaces, or forced exercise at a young age can damage soft joints.
-
Repetitive strain before the bones have fully ossified increases risk.
-
Poor Breeding Practices
-
Breeders who don’t test for joint health (e.g., OFA certification) increase the likelihood of dysplasia in offspring.
-
Breeding dogs with even mild signs of dysplasia can pass on the defect.
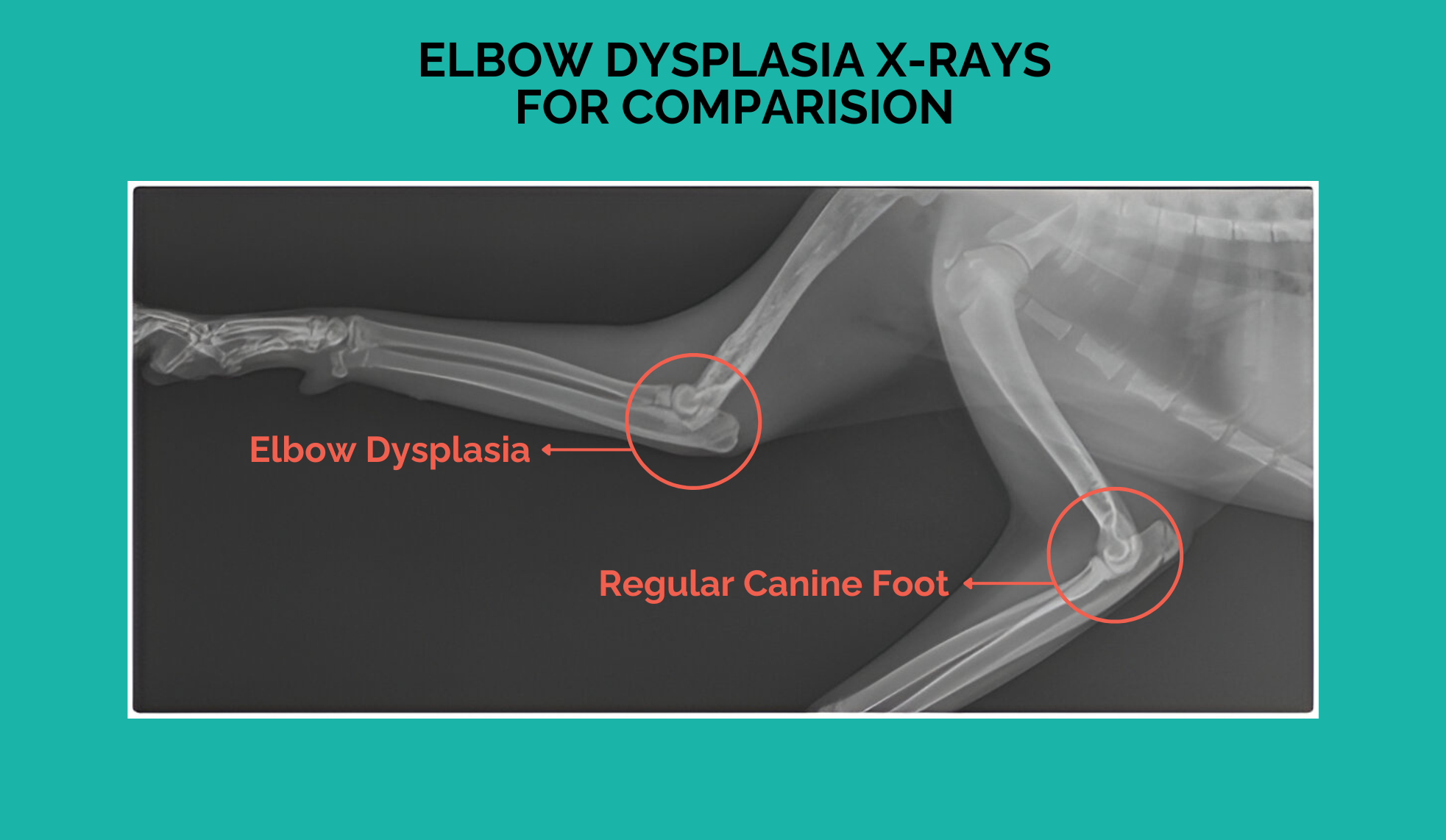
How Does It Affect the Dog?
Hip and Elbow Dysplasia both can have major effects on your pet, which include:-
-
Lameness and Limping
-
Often seen in one or both limbs.
-
May start mildly and worsen over time or after intense activity.
-
Stiffness and Reduced Range of Motion
-
Dogs may resist flexing or extending joints.
-
Movements like climbing stairs or getting in a car become difficult.
-
Pain and Sensitivity
-
Dogs may yelp when touched near the joint or avoid being handled.
-
Behavioural changes like irritability, restlessness, or even aggression can occur due to chronic pain.
-
Decreased Activity and Endurance
-
Dogs may tire quickly, refuse walks, or lie down more frequently.
-
Young dogs may appear lazy when they're in discomfort.
-
Muscle Atrophy
-
Muscles, especially in hind limbs (hip dysplasia) or forelimbs (elbow dysplasia), shrink due to disuse.
-
Creates a noticeable difference in leg girth.
-
Gait Abnormalities
-
Bunny-hopping gait (hips) or outward turning of the elbow.
-
Uneven or swaying walking patterns.
-
Arthritis and Inflammation
-
Chronic wear and tear causes osteoarthritis.
-
Leads to swelling, joint thickening, and long-term disability if unmanaged.
How to Prevent or Minimise the Risk of Hip or Elbow Dysplasia?
While some causes are genetic and not fully preventable, proactive care helps reduce risk and delay progression.
-
Choose Reputable Breeders
-
Only adopt from breeders who test for dysplasia (OFA or PennHIP certification).
-
Avoid backyard breeders or those focused solely on appearance or size.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight
-
Keep your dog lean throughout life. Overweight dogs show earlier and more severe symptoms.
-
Regular weight checks and diet control are crucial.
-
Feed Appropriate Puppy Food
-
Large-breed puppy formulas are specially designed to control growth rate.
-
Avoid supplements unless prescribed, as excess calcium or vitamins can do harm.
-
Avoid Excessive Exercise During Growth
-
No forced jogging or jumping before 12–18 months.
-
Allow for natural play and low-impact activity on soft surfaces.
-
Joint Health Supplements
-
Starting early with Glucosamine, Chondroitin, MSM, or Omega-3s can support joint lubrication and inflammation control.
-
Our Canine Mobility+ is a powerful supplement designed to enhance flexibility, ease stiffness, and promote long-term mobility. It has been carefully curated to ensure it supports overall musculoskeletal wellness with every dose for both senior dogs and young and energetic breeds.
-
Regular Veterinary Monitoring
-
Early X-rays (around 4–6 months for the elbow and 6–12 months for the hips) can help catch issues early.
-
Interventions like physical therapy, pain management, or surgery can slow progression.
Which breeds are prone to Hip and Elbow Dysplasia?
Hip Dysplasia and Elbow Dysplasia are prevalent in larger dog breeds and high-energy or active breeds. Large breeds such as German Shepherd, Labrador, Great Dane, Golden Retriever, Rottweiler, St. Bernard, Bernese Mountain Dog, American Bulldog, Mastiff breeds and the Boxer.
Active or high energy breeds such as the Greyhound, Saluki, Border Collie and the Belgian Malinois are prone to hip and elbow dysplasia due to either high impact exercises as a puppy or even certain injuries.












Leave a comment